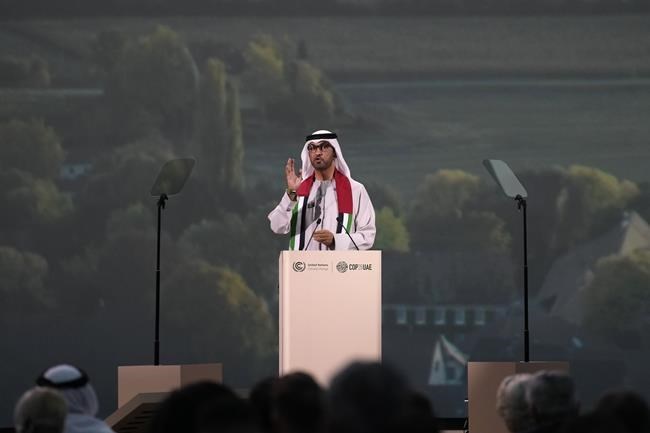
DUBAI, United Arab Emirates (AP) — Fifty oil companies representing nearly half of global production have pledged to reach near-zero methane emissions and end routine flaring in their operations by 2030, the president of this year's United Nations climate talks said Saturday, a move that environmental groups called a “smokescreen."
The announcement by Sultan al-Jaber, president of the climate summit known as COP28 and head of the Abu Dhabi National Oil Co., comes as he and others have insisted his background would allow him to bring oil companies to the negotiating table. Al-Jaber has maintained that having the industry's buy-in is crucial to drastically slashing the world’s greenhouse emissions by nearly half in seven years to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) compared with pre-industrial times.
The pledge included major national oil companies such as Saudi Aramco, Brazil's Petrobras and Sonangol, from Angola, and multi-nationals like Shell, TotalEnergies and BP.
“The world does not work without energy,” said al-Jaber. “Yet the world will break down if we do not fix energies we use today, mitigate their emissions at a gigaton scale, and rapidly transition to zero carbon alternatives.”
Methane can be released at several points along the operation of an oil and gas company, from fracking to when natural gas is produced, transported or stored. Over a shorter period, it’s more than 80 times more powerful than carbon dioxide, the greenhouse gas most responsible for climate change.
For months leading up to COP28, there has been talk that one of the biggest outcomes could be on methane. Not only do methane leaks, along with flaring, which is burning of excess methane, and venting of the gas all contribute to climate change, but these problems can largely solved with current technologies and changes to operations. Indeed, oil and gas companies could have taken such measures years ago but largely have not, instead focusing more on expanding production than focusing on the byproduct of it.
In that way, the methane deal represented a potentially significant contribution to combatting climate change that largely maintained the status quo for the oil and gas industry. Environmental groups were quick to criticize it.
The pledge is a “smokescreen to hide the reality that we need to phase out oil, gas and coal,” said a letter signed by more than 300 civil society groups.
Marcelo Mena, CEO of Global Methane Hub, rejected that the notion that having near-zero methane emission commitments was a way to delay a phase out of fossil fuels.
“We wouldn’t let oil companies leak into the ocean until phase out, so why would we let them leak out methane to super charge climate change?” said Mena, a former environment minister in Chile.
Still, Mena said that self-reporting didn't go far enough to push oil and gas companies to make changes. Instead, he said putting a price on pollution, or companies finding themselves shut out of markets that require high standards with leaks, would force change.
Stricker regulations are beginning to take hold. On Saturday, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency issued a final rule aimed at reducing methane emissions and other harmful air pollutants generated by the oil and gas industry. It targets emissions from existing oil and gas wells nationwide, rather than focusing only on new wells as previous EPA regulations have done. It also regulates smaller wells that will be required to find and plug methane leaks.
Earlier this year, European Union negotiators reached a deal to reduce methane emissions from the energy industry across the 27-member bloc. The agreement bans routine venting and flaring, and mandates strict reporting. By 2027, it will expand those norms to oil and gas exporters outside the bloc.
Saturday's announcement did not address the oil and natural gas being burned off by the end users, whether motorists in their cars or by plants powering cities. That burning off creates the greenhouse gases fueling climate change.
The Oil and Gas Decarbonization Charter is backed by both the United Arab Emirates and neighboring Saudi Arabia, two OPEC heavyweights. Saudi Arabia’s vast oil resources, located close to the surface of its desert expanse, makes it one of the world’s least expensive places to produce crude. Both Abu Dhabi’s ADNOC and Saudi Aramco, the world’s third-most-valuable company, have signed onto the pledge.
Separately, organizers said 110 countries have signed onto a pledge to triple the world’s installed renewable energy capacity by 2030, something pledged in September by leaders of the so-called Group of 20. Their countries emit 80% of all planet-warming gases.
____
Associated Press climate and environmental coverage receives support from several private foundations. See more about AP’s climate initiative here. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Jon Gambrell, Peter Prengaman And Seth Borenstein, The Associated Press